Internet Of Things (IoT) Features & Benefits
What is Internet Of Things?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is an ecosystem of connected physical objects that can be accessed through the Internet. The’ thing’ in IoT could be a person with a heart monitor or a car with built-in sensors, i.e. objects that have been assigned an IP address and are capable of collecting and transferring data over a network without manual assistance or intervention. Embedded technology in objects enables them to communicate with inner states or the external environment, which in turn impacts choices taken.
Why Internet Of Things?
The Internet of Things enables individuals to live and operate smarter and to achieve full control over their life. In addition to providing smart devices for home automation, IoT is vital for the company. IoT offers companies with a real-time look at how their systems really operate, providing insights into everything from machine efficiency to supply chain and logistics activities.
IoT allows businesses to automate procedures and decrease labor costs. It also reduces waste and increases service delivery, making it cheaper to produce and deliver products and providing transparency in client operations.
IoT affects every sector, including healthcare, finance, retail, and production. Smart cities assist people to decrease waste and energy consumption and linked sensors are even used in agriculture to assist monitor crop and livestock yields and predict growth trends.
Benefits from Internet Of Things
The Internet of Things offers several benefits to organizations, allowing them to:
- Monitor their overall business processes;
- Improve the customer experience;
- Save time and money;
- Enhance employee productivity;
- Integrate and adapt business models;
- Make better business decisions; and
- Generate more revenue.
IoT promotes companies to rethink how they approach their businesses, sectors, and markets and provides them with instruments to enhance their business strategies.
Internet Of Things standards and frameworks
There are several emerging IoT norms, including: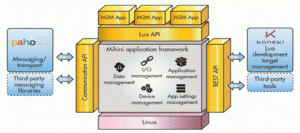
- 6LoWPAN (IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks), an open standard established by the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). The 6LoWPAN standard allows any low-power radio to interact over the Internet, including 804.15.4, Bluetooth Low Energy and Z-Wave (for home automation).
- ZigBee0 is a low-power, low-speed wireless network used mainly in industrial settings. ZigBee is based on an IEEE 802.15.4 standard. The ZigBee Alliance has created Dot dot, the universal IoT language that enables smart objects to work securely on any network and to understand each other.
- LiteOS is a Unix-like operating system for wireless sensor networks. LiteOS promotes smartphones, wearables, smart manufacturing apps, smart homes and the Internet of Vehicles (IoV). The operating system also serves as a platform for the growth of smart devices.
- OneM2 M is a machine-to-machine service layer that can be integrated into software and hardware for connecting devices. A global standardization body, OneM2 M, has been set up to create reusable norms to allow IoT apps to interact across distinct vertical lines.
- DDS (Data Distribution Service) has been created by the Object Management Group (OMG) and is an IoT standard for real-time, scalable and high-performance machine-to-machine interaction.
- AMQP (Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) is an open-source released standard for wireless asynchronous messaging. AMQP allows encrypted and interoperable messages between organizations and apps. The protocol is used for client/server communication and IoT device management.
- CoAP (Constraint Application Protocol), a protocol developed by IETF that specifies how low-power computing systems can function on the Internet of Things.
- LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network), a protocol for large area networks, is intended to help large networks, such as smart cities, with millions of low-power devices
How does it work?

Devices and items with built-in sensors are linked to the Internet of Things platform, which integrates data from distinct devices and uses analytics to share the most precious information with apps designed to meet particular requirements.
These strong IoT platforms can pinpoint precisely what data is helpful and what can be securely ignored. This data can be used to identify trends, to create suggestions and to identify possible issues before they happen.
For instance, if I own a vehicle manufacturing company, I might want to understand which optional parts (for instance, leather seats or alloy wheels) are the most popular. Using technology from the Internet of Things, I can:
- Use sensors to identify which regions in the showroom are the most popular and where clients stay the longest.
- Drill down the sales information accessible to define which parts are selling the fastest.
- Automatically align sales information with supply, so that common products do not go out of inventory.
Internet Of Things Future
There is no shortage of IoT market estimates. For instance, a few of them include:
- Bain & Company expects annual IoT revenues from hardware and software to exceed $450 billion by 2020.
- McKinsey & Company estimates that IoT will have an effect of $11.1 trillion by 2025.
- IHS Markit thinks that the amount of connected IoT appliances will rise by 12 percent annually to reach 125 billion by 2030.
- Gartner estimates that 20.8 billion linked goods will be used by 2020, with complete IoT devices and services spending to reach $3.7 trillion by 2018.